Physical Processes
Today's WEATHER in EAST ASIA
Using satellite imagery and maps, The Weather Channel provides forecast maps for Asia. Students can use these maps to reflect on analogous weather data at their home location.
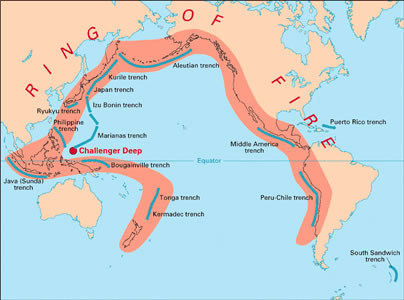
JAPAN: Plate Techtonics and the "RING OF FIRE"
Volcanoes and earthquakes, tsunamis, and typhoons are among the most powerful natural features that shape and reshape lives in East Asia. The Asian "Ring of Fire" is part of a system that circles the Pacific Basin. The Ring of Fire contains 75% of the Earth's active and dormant volcanoes, and it is the location of 90% of the world's earthquakes.
Plate Techtonics and the Ring of Fire [National Geographic]
Ring of Fire [National Geographic] article for grades 5-8
This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Techtonics [United States Geological Survey]
An online edition of text and images full of detailed information providing a rich research resource for teachers and students. Although the information is not focused on East Asia, it is useful background for understanding the geological formation of the region. For grades 9-12. Becoming educated in physical geography requires an understanding of the theory of plate tectonics and the Earth's geological history. In this lesson, students will learn more about these concepts as they investigate the region known as the Ring of Fire.Savage Earth [Thirteen, PBS] A comprehensive four-part look at the forces that continue to affect the Earth. This website includes dramatic animation and video clips.
- Can we Predict a Tsunami? Teacher Guide - Lesson Plan [Stevens Institute of Technology: Center for Innovation in Enginnering and Science Education]
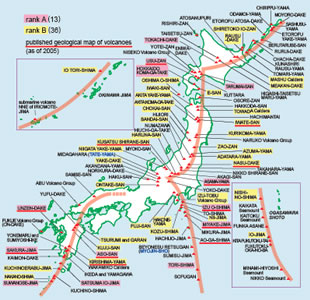
Japan's Active Volcanoes
Within the tight confines of Japan's four major islands, there are a large number of active volcanoes. Mt. Fuji and other volcanoes are the result of the subduction of the Pacific plate under the Eurasian plate within the "Ring of Fire.” While some parts of Japan's volcanic backbone are quiet, like Mt. Fuji, others are violent, such as the volcano at Sakurajima in Kagoshima, Kyushu.
 OutdoorJapan.com live webcam view of Mt. Fuji
OutdoorJapan.com live webcam view of Mt. Fuji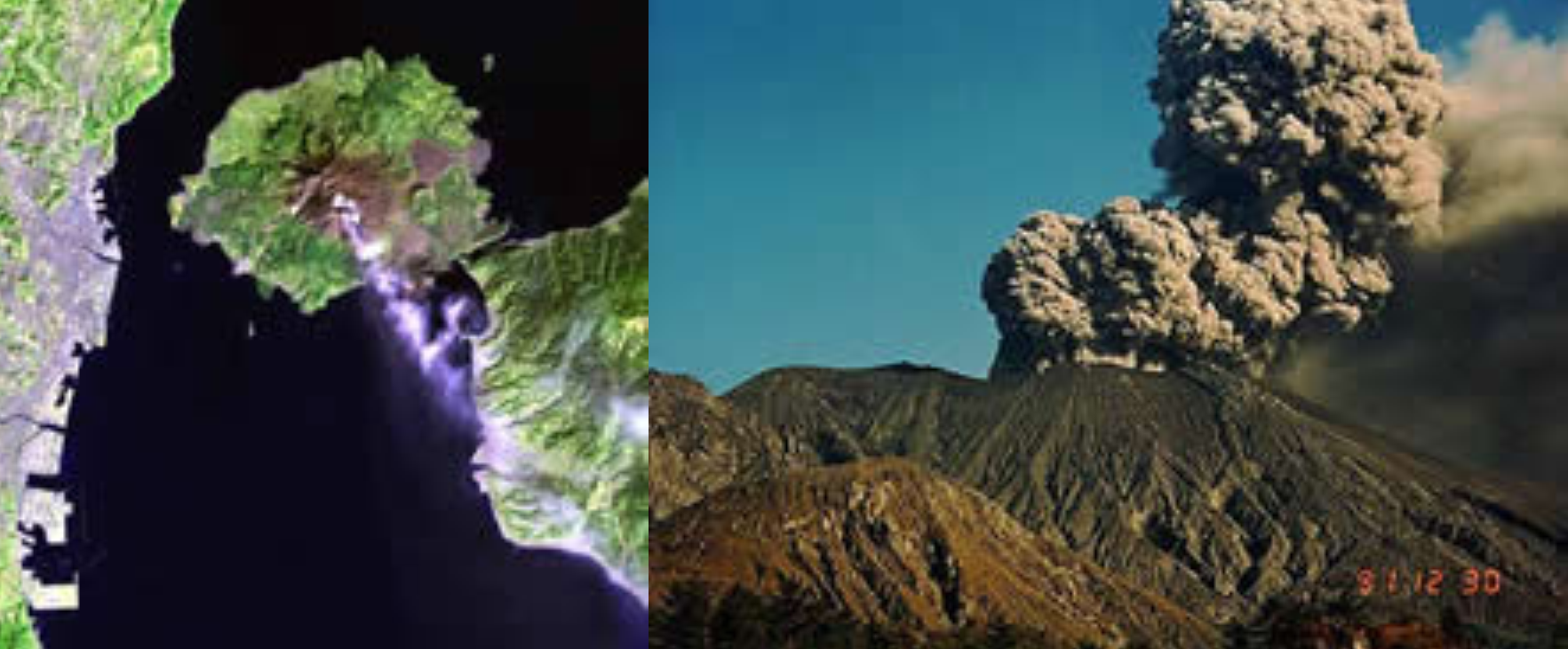 Images of Sakurajima
Images of SakurajimaCHINA
Mountains & Deserts
-
The west of China is comprised of mountains and deserts as well as plateaus that do not provide much arable land for agriculture.
Throughout most of history, the civilization that grew up to the east in what is today China was not surrounded by other nearby major civilizations. To this extent the Chinese were "isolated" from competing civilizations, although there was a broad and fluid frontier zone on the western margins. This geographical fact is important to remember when discussing the Western encroachment on China from the sea during the late imperial period.
Although the mountains and deserts of the west limited contact between early imperial dynasties and other centers of civilization in the Inner Asia, Middle East, South Asia, and Europe, there were some important and notable exchanges of culture. The legendary Silk Road facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between China and each of these areas.
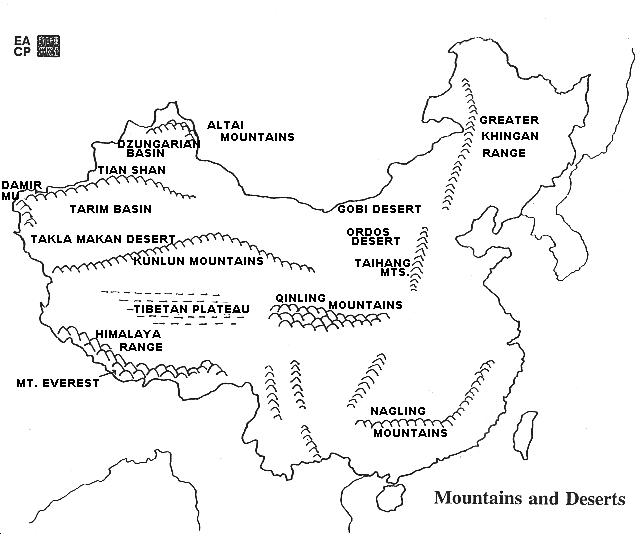
[AFE: CHINA'S GEOGRAPHY and outline map of China's mountains and deserts]
Why was China's early civilization relatively isolated from other early civilizations?
What sort of terrain did the eventual route between early China and other civilizations follow?
Major Rivers
-
China's two major rivers, the Huang He (Yellow River) and the Chang Jiang (Yangzi or Yangtze River), as well as the Pearl River (Zhu Jiang) delta system marked by the Xi Jiang (West River) in southeastern China, have provided the framework for agricultural development and population growth throughout China's history.
-
Another river, the Heilong Jiang (known also as the Amur River, its Russian name) marks the border between China and Russia; at times in the past, this area was one of confrontation between the neighbors.
-
The drainage basins of China's rivers differ in terms of extent and topography, offering varying opportunities for agricultural development.
-
Because some of China's largest rivers have their source regions on the high Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and drop great distances over their middle and lower courses, China is rich in hydroelectric resources. ... Read more in the Asia for Educators teaching unit, "China's Geography."
Course Changes of the Yellow River
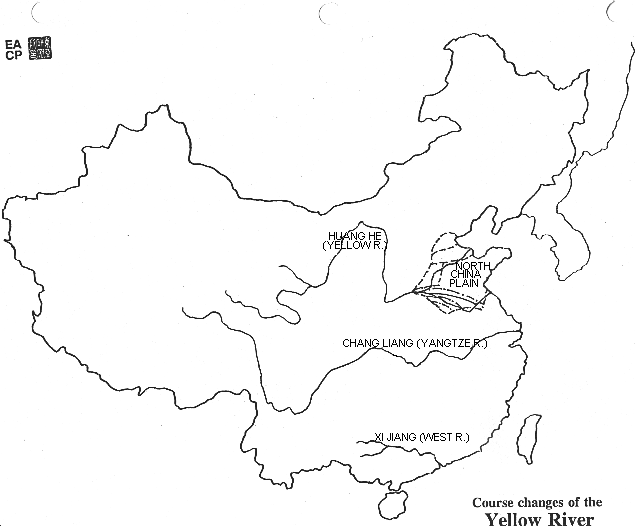 Course Changes of the Yellow River
Course Changes of the Yellow River[AFE: CHINA'S GEOGRAPHY and outline map of China's major rivers.]
Can you name China's major rivers?
Huang He (Yellow River)
Why is this river called a "yellow" river?
Why is this river called "China's Sorrow"?
What is loess? How is it useful for human habitation?
Chang Jiang (Yangzi or Yangtze River)
Why is this river called China's "main street"?
In what part of China are the upper reaches of this river?
Why is happening in the area called "The Three Gorges"?
-
Zhu Jiang (Pearl River)
What kind of land surrounds this river?
What is grown in this river's ecosystem?
-
Research questions involving all the readings and maps about China's rivers:
If you wanted to travel in China with a row boat, which river would you choose to go on and why?
Could you travel by boat from one river to another without going into the open sea or carrying the boat across land? Which parts of China would you see if you did this?
KOREA
Geography of KOREA [Korea Society]
VIETNAM: Rivers and Waterways
Voyage to Vietnam: Rivers and Waterways [Children's Discovery Museum, San Jose]
Ecosystems and Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is now the mantra heard in East Asia, just as it is heard elsewhere in the world. Indeed, the earth's ecosystems transcend political boundaries and must be viewed within a global context. As populations grow and increasingly consume land, water, and other raw materials, ecosystems of every type are stressed and sometimes irreversibly transformed.WATER Issues (see also Humans Modify Physical Systems)
CHINA: Water Issues and Controlling the Rivers
Rebirth along China's Yangtze River [World Wildlife Fund]
Water Issues in China [SPICE Digest, Stanford University]
This article by Rylan Sekiguchi explores China's seemingly insatiable thirst for water, a basic resource that has been depleted in some areas and heavily polluted in others. Many claim that China has a fundamental water crisis of unparalleled proportions. Excerpted from the SPICE publication 10,000 Shovels: China's Urbanization and Economic DevelopmentH2O: The Molecule that Made Us - Part 2: Civilizations (video) [PBS]
“Civilizations" - Travel into the past to see how water may have driven our own evolution — and created civilizations, along the banks of great rivers, including the Yellow River in China. But can the Earth's water supplies guarantee our future?
VIETNAM and the MEKONG DELTA
"The Mekong River with Sue Perkins" [PBS] (On your local PBS station)
“The Mekong has many names. In China it's known as the Lancang Jiang, meaning 'turbulent river'. The Thai and the Lao refer to it as Mae Kong or Mae Nam Kong, meaning 'mother water'. And the Vietnamese call it Cuu Long, meaning 'nine dragons', in reference to where the river splits into multiple branches in the delta.”…“The Mekong is South East Asia's greatest river, the Mother of Water that brings life to millions of people from the paddy fields of Vietnam to the mountains of the Tibetan Plateau. In this series, Sue Perkins goes on an extraordinary journey, spanning nearly 3,000 miles, to explore lives and landscapes on the point of enormous change….Sue's epic journey begins in Vietnam on the vast Mekong Delta… And when Sue reaches her final destination – China, home to the source of the Mekong – she witnesses change sweeping through faster than any other Mekong nation, as China's economic miracle transforms even the remotest regions.”
Environmental Sustainability of East Asia's Resources
Journey to Planet Earth [PBS]
This website includes teachers' materials, educational links, video excerpts, and "stories of hope" that focus on individuals and the regions within which they live. The series literally covers the world to comprehensively examine global environmental change, including places in Asia and Latin America, with a strong focus on the interrelationships between geographic and other factors.Earth Trends [World Resources Institute]
EarthTrends is a comprehensive research website for the following topics, with a searchable database, maps, country profiles, features, and data tables under each topic: USE Search function, then “Maps” in right-hand bar.Coastal and Marine Ecosystems
Water Resources and Freshwater Ecosystems
Climate and Atmosphere
Population, Health and Human Well-being
Economics, Business and the Environment
Energy and Resources
Biodiversity and Protected Areas
Agriculture and Food
Forests, Grasslands and Drylands
Environmental Governance and Institutions
China
Hong Kong
Japan
Korea (North)
Korea (South)
Taiwan
Vietnam
Each of the topics above offers "Country Profiles" on the East Asian countries/areas listed below: